Keyword Research Framework: How I went from 0 to 1.5M visits/month
Get my 7-step keyword research framework - how to get the right list of keywords, which tools to use, and where to get all your related keywords and phrases.
Published November 5, 2024

I absolutely love SEO! It's one of the MOST reliable marketing channels for a startup. I've used SEO to grow my startups to 1.5M visitors every month and $3M in revenue. Entirely bootstrapped :)
But SEO requires you to invest heavily in terms of time & money. And you need to have patience to see the results. It's a marathon, not a sprint.
So, it's key that you have robust SEO processes to drive your growth. Today, I will be sharing the SEO frameworks I used to grow my startups and focus on the keyword research part of SEO.
Let's dive in!
But first, why should you care about SEO?
SEO can be your biggest organic channel. 5.6 billion searches take place on Google every single day! So, Google search can be a key channel to bring relevant visitors to your website and then convert them into paying customers.
Here are just a few reasons you should invest in search engine optimization this year:
1. Search has huge potential
Search isn’t going anywhere. 5.6 billion searches per day translate to 2 trillion searches every year, and that's a huge audience to present your product to. If you're not serious about SEO, you're missing out on so many potential customers.
2. Searchers have high Intent
Every search on Google is performed with a specific intent. In SEO terms, we call it 'searcher intent' and it's classified into different types like informational, commercial, transactional, etc.
For example, when you search for 'Nike shoes', it's likely that you want to buy Nike shoes (commercial intent). Whereas when you search for 'do Nike shoes last long?', you want information on the specific topic (informational intent).
As a business owner, you can create content to target these specific audience segments based on their intent and get highly relevant customers into your marketing funnel.
3. Inbound traffic
With SEO, your users will organically find you on search engines. Unlike sales or outbound marketing, you don't have to constantly nudge your potential customers to buy from you.
Instead, you provide value by creating quality, useful content and Google does the job of sending users to your product or website.
4. Search traffic is evergreen
A tweet may do well for a few hours, and a LinkedIn post may do well for a few days at max. But an article that ranks on Google can bring you consistent traffic for 12-24 months and beyond.
Of course, you still need to update the content periodically and signal the freshness of content to Google. But the maintenance effort is minimal.
With SEO, if you invest heavily upfront and then periodically update your content, you can reap the benefits of consistent traffic forever.
How I grew my startups to 1.5M visits/mo with SEO
I have bootstrapped my startups to $3M in revenue over 5 years, and SEO has been a key growth driver for us.
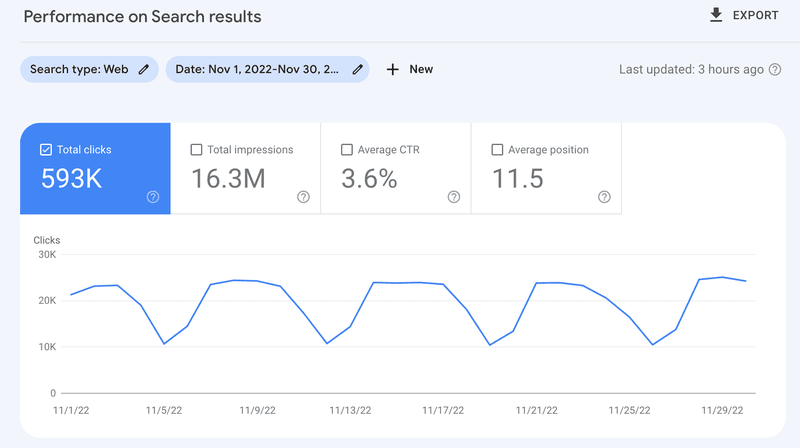
My primary startup, Flexiple, gets ~600,000 organic clicks every month.
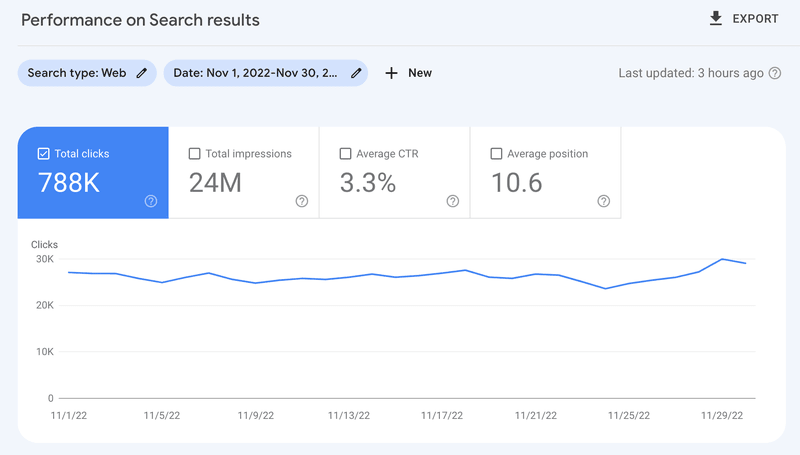
And, my second startup, Remote Tools, gets ~800,000 organic clicks every month.
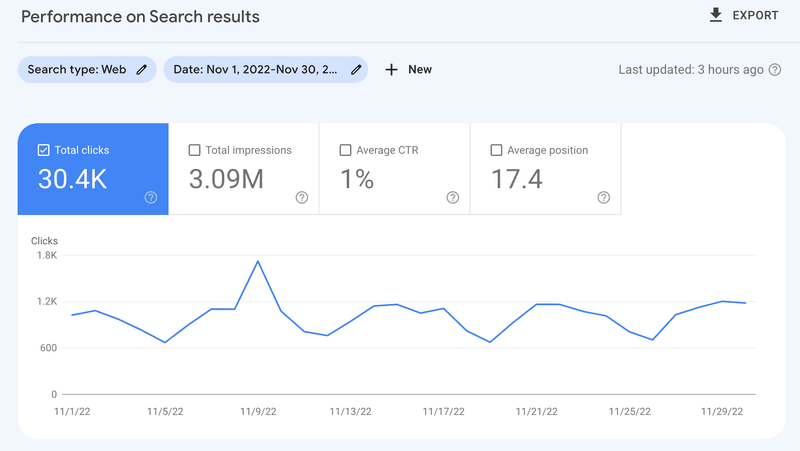
Finally, my most recent startup, Buildd, is just picking pace and gets ~30,000 organic clicks every month.
All of these numbers look great on paper, but it took us years of experimentation & hard work across all areas of SEO to crack these results.
To quickly summarise the areas we cracked:
1. Domain Authority: We realized early on that domain authority is key to rankings on SEO. So, we doubled down on authentic link-building for our websites and we now have a link-building engine that helps us consistently build links for my startups.
2. Keyword Research: We built our own keyword research process that helps us identify topics we can write pieces of content on, such that there's a high chance to beat our competitors.
3. Internal Linking: Internal linking is one of the most powerful yet ignored aspects of SEO. The great thing is that it's entirely in your own control. So, we have devised our own mini frameworks to effectively create content hubs or semantic content networks on our websites.
4. Analysis & content refreshes: At the scale of 1.5M visits/month, we need an effective framework to regularly track metrics for our existing & new content. We track numbers in an automated fashion using Google Data Studio (using Google Search Console & Google Analytics as data sources), and have triggers for updating & optimizing old content.
So let’s talk about keyword research.
Keyword research: the most critical part of your SEO process
When we first worked on content marketing, we focused entirely on writing quality. We wrote informative blog posts without doing any research about topics or keywords. Our naive assumption back then was that users would somehow stumble upon our content and be floored by the quality.
You would have easily guessed the result - ZERO users, tons of wasted effort & money.
So, if you want Google to rank your website for specific queries and send users to your pages, you need to extensively research keywords & topics.
The good news is that we have been doing this for 3+ years now and you can build upon our well-tested knowledge to find relevant keywords for yourself.
In the following sections, I will focus on and dive deep into our very own effective keyword research process.
My 7-step keyword research process for SEO
The most important thing to remember in SEO is that the search results page is your battleground and you need to beat your competitors i.e. outrank or replace the already ranking websites. You also don’t need to be a top-notch SEO specialist to do this right.
The following framework will help you find a goldmine of lucrative, low-competition keywords.
I ran a website & newsletter around remote working for 3 years. So I will take the example of 'remote working' as a business area to show how the keyword research method works.
Step 1: Come up with seed keywords
The first step is to come up with your seed keywords. These are keywords, topics, or even broad themes related to your startup or business. They are the ones you already know or have read about.
Make a list of all the terms or topics relevant to your business
Let’s take 'remote working', the top seed keywords I can think of are the following:
- remote work
- work from home
- digital nomad
- backpacking
- telecommuting
- asynchronous communication
If you can't come up with seed keywords on your own, you can look at your competitors you know and see what topics they write pieces of content on.
For our example, I know that websites for remote working jobs are my top competitors and they write pieces of content on topics like "remote work jobs", "remote team culture" etc. All of these topics can be added to our seed keywords list.
Step 2: Search for keywords on Wikipedia & Quora
Wikipedia is a storehouse of information and even Google uses Wikipedia data on a lot of search results.
So, Wikipedia is a great place to find out what additional topics you can write about in your niche or business area.
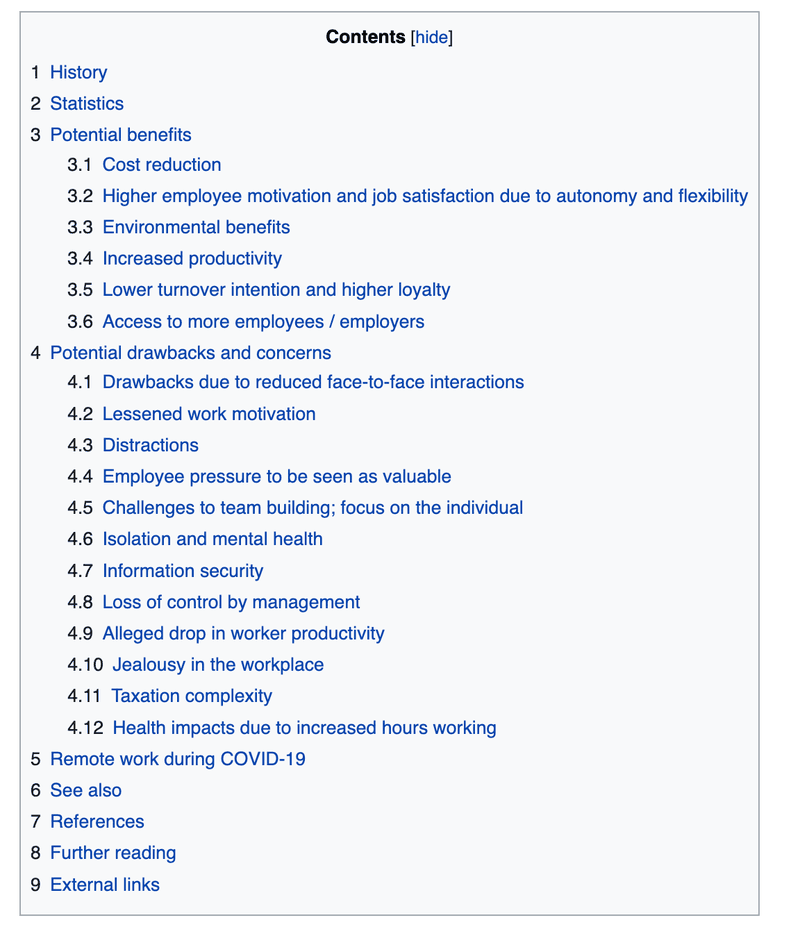
Let's head over to the Wikipedia page for 'remote work' and look at the table of contents.
You can see that the table of content for a single page gives us so many target keywords and topic ideas.
- Benefits of remote working
- Drawbacks of remote working
- Environmental benefits of remote working
- Mental health effects of remote working
- Remote work during Covid-19
... and the list goes on.
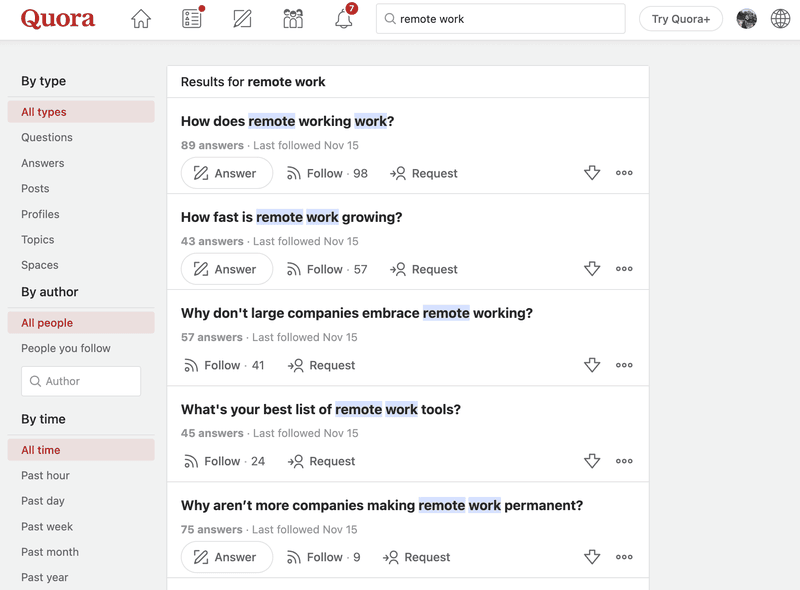
Similarly, Quora is another great place to know what information real users are seeking.
When I search for 'remote work' on Quora, these are the common questions that pop up.
And, here are some keywords you can immediately identify:
- List of remote work tools
- Best remote working tools
- Is remote working good?
- Will big companies embrace remote working?
When you click on a question, you will see a bunch of related questions for even more ideas for potential keywords.
Step 3: Use a keyword research tool
Till now, we were mostly searching for ideas and using our own intuition & logic to identify topics.
It's now time to use the power of SEO tools to expand our initial list exponentially!
I've personally used Ahrefs all along and found it to be an excellent tool. But there are other helpful tools available as well like SEMRush. Google also has its own tool, Google Keyword Planner, which gives you a range for traffic potential for any keyword. There are also Chrome extensions for keyword research you could use.
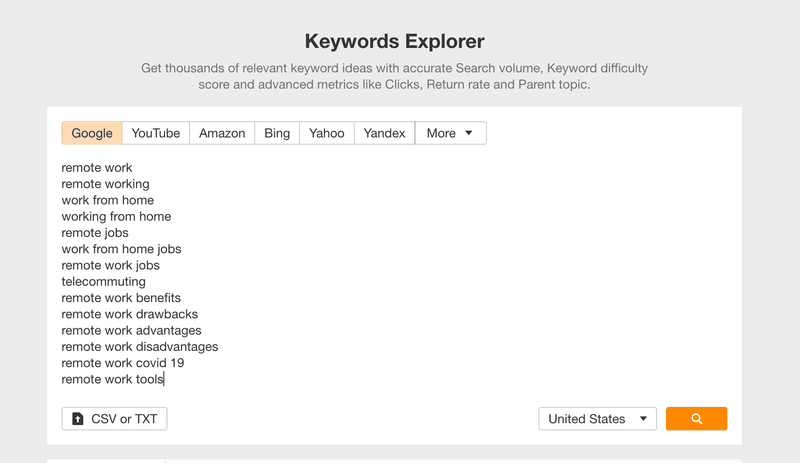
Let's head over to the "keyword explorer" on Ahrefs and enter the list of seed keywords we found.
After you hit submit or search, you'll see all the metrics for the keywords you entered.
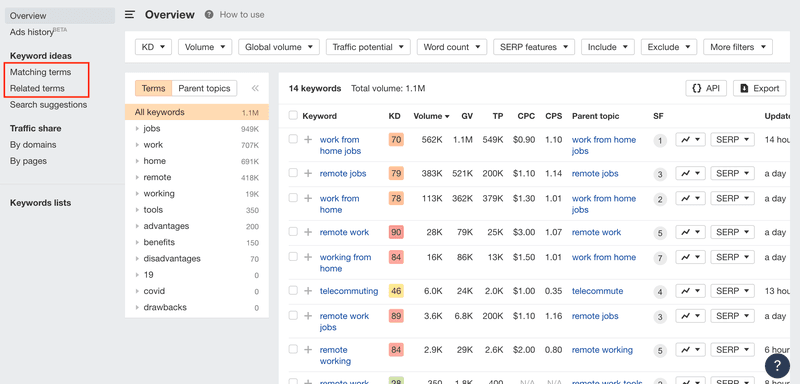
Next, you can use either 'matching terms' or 'related terms'.
Matching terms: This gives you all the keywords that match at least one of the phrases from your list. For example, "best remote jobs" is shown as a matching term because "remote jobs" was part of our seed keywords list.
Related terms: This gives you all the keywords that are related to your seed keyword list. These keywords may or may not contain any of the initial phrases you entered. For example, "amazon jobs" & "monster jobs" are shown as related terms to "remote jobs".
I recommend using 'matching terms' first, and then trying 'related terms' in the second iteration of this process.
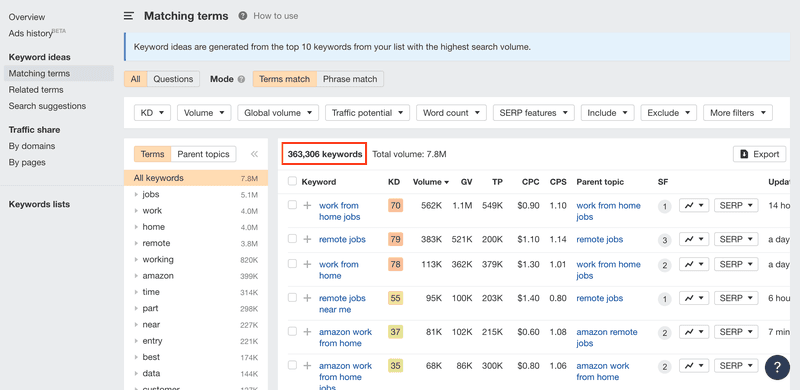
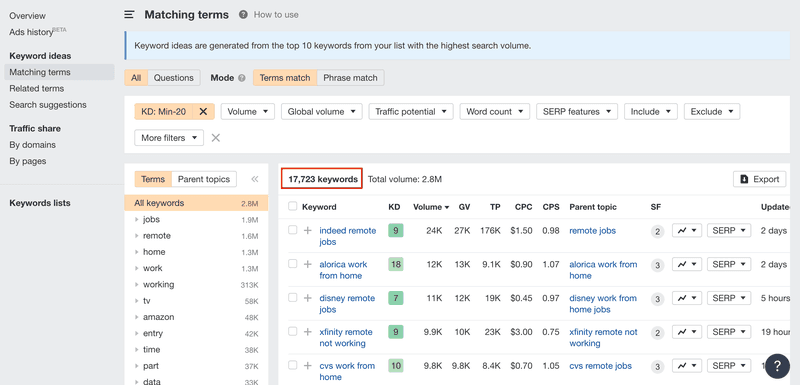
So, after using 'matching terms', we get a huge list of 360,000+ keywords to play with!
Step 4: Filter for keyword difficulty
Now, it's time to narrow down to the best keywords from this list.
There are a couple of things you can do next:
1. Filter for low difficulty
All SEO tools have their own metric to indicate keyword difficulty or KD. KD is basically a heuristic that indicates how easy or tough it is for any website to rank on search engines. So, high-KD keywords will have the highest competition.
If you're just starting out with SEO, I'd recommend choosing a KD of 10 or 20 to start with. This will give you keywords with the lowest competition.
After applying the filter of KD<20, our list of 360,000+ keywords is drastically reduced to less than 18,000 keywords.
2. Identify themes or groups of keywords
You can manually sift through the list and try to identify patterns among the keywords.
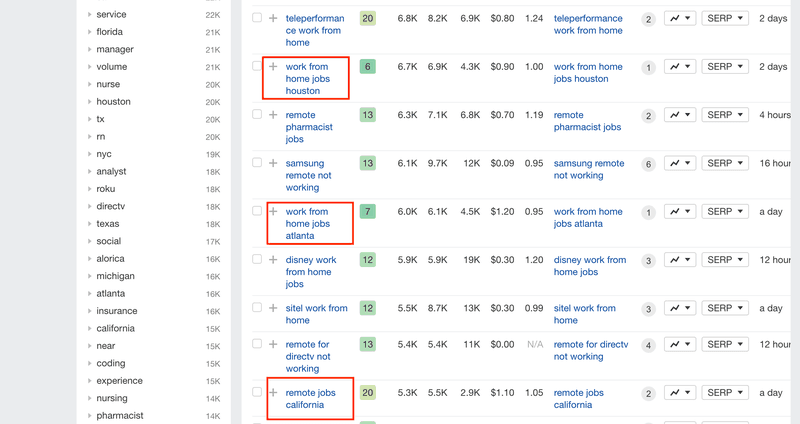
For example, I can see that the list contains a lot of keywords with the pattern "work from home jobs <location>" or "remote jobs <location>" (eg. remote jobs san diego).
Step 5: Filter for search volume
We will now further narrow down the list of keywords using the monthly keyword search volume.
There are two ways to go about this:
1. Low to medium search volume
For keywords with low to medium search volume (eg. <=100 on Ahrefs), search engines are more open to experimenting with the ranking results. So, it's faster to rank for such keywords vs. high-volume keywords.
Google doesn't reveal this officially, but there's anecdotal evidence online and I've observed this personally as well.
So, if you're just starting with a new website or business, you can filter for low to medium search volume so that you see results faster. Such keywords are also called long-tail keywords.
2. High search volume
On the contrary, if you have an established business or a website with moderate to high authority (eg. >30 DR), you should target high-volume keywords.
When you publish content around a high-volume keyword and optimize it correctly, search engines will automatically rank you for a bunch of related secondary keywords.
Step 6: Manually check if the search intent aligns
This is a key step in the process and requires manual effort again.
Search intent is by far the most critical aspect when you write SEO focussed content. For example, if the top-ranking pages for "work from home jobs" are actual job listing websites, you will not rank well if you write a regular blog post.
Search intent tells you the user's intention behind searching for a particular keyword.
There are 4 types of search intent:
- Informational intent — the user wants to gain information about something (eg — "what is a marketing consultant", "why should I hire a digital marketing agency”)
- Commercial investigation intent— the user is searching for information with the intent to buy a product or service. (eg — "best accounting software")
- Transactional or purchase intent — the user actually wants to buy a product or service. (eg — "Mailchimp coupon" or "men's Nike air max 270")
- Navigational intent — the user wants to go to a particular website or page. (eg — "youtube.com")
Every search query or keyword has a particular user intent associated with it and it’s important to design the page (and the content) to align with that intent.
That’s why you should manually check the top ten search results for:
- Search intent — informational, commercial investigation, transactional, navigational
- Type of content— blog posts, eCommerce pages, landing pages, company website
- Format — listicles, tutorials, opinion pieces, how-to’s
Step 7: Check website authority for top 10 results
As I said earlier, the Google search results page is your battleground and your aim is to kick out & replace one of the top 10 results.
The domain authority is a good proxy to know whether you can achieve this. If there are one or more websites in the top ten results that have a lower authority than your website, it's likely that you can outrank them.
Here's how you can do this:
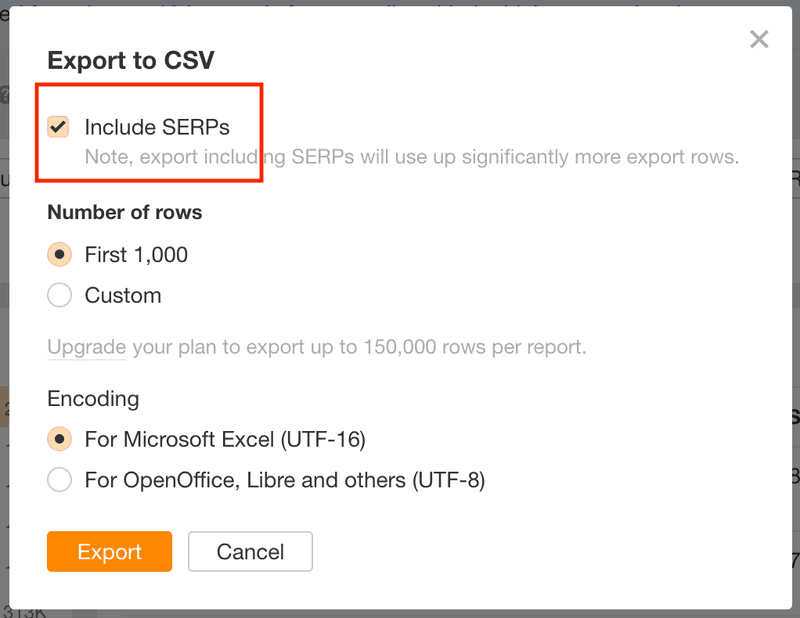
1. Take your list of keywords and export the SERP data from Ahrefs.
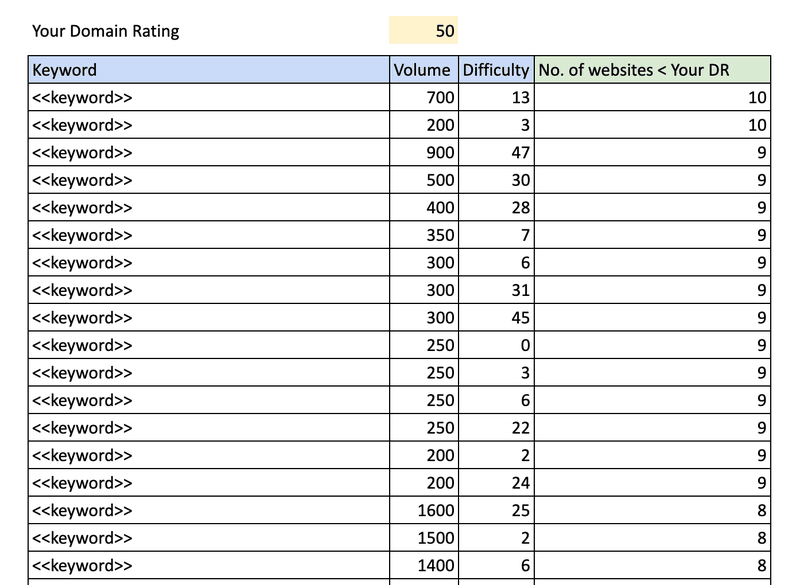
2. Once you have the CSV with all ranking results, use a simple formula in Google sheets or Excel to find out the number of ranking websites that have a lower authority than your website. You can then sort the results in descending order based on this metric.
Your sheet should look like this:
Leverage your keyword goldmine
Now that you've your goldmine of keywords, your next step should be to prepare a content strategy that involves your content calendar, planning & designing your web pages, and internal linking & distribution.
While keyword research is one of the most crucial parts of the SEO strategy, you still need to cover all other areas to get results. It's also key to understand that a key success metric from your SEO efforts shouldn’t just be the traffic you get to your website.
Your content should also bring you qualified leads and paying customers. For that, you need to focus equally on conversion rates. Need help applying this framework? Find the perfect SEO consultant for your business through Mayple!